How to read the graph
Natural environmental background radiation
In the guided mode only, the blue area of the graph denotes a range of values usually measured in the environment where no basic nuclear installation (INB) impacts the measurements: this is the environmental background radiation (see the Background noise section). It is also referred to as one of the national reference values (National background radiation not affected by any installation). It includes natural radioactivity, plus artificial radioactivity due to the remanence of the Chernobyl accident and atmospheric nuclear tests.
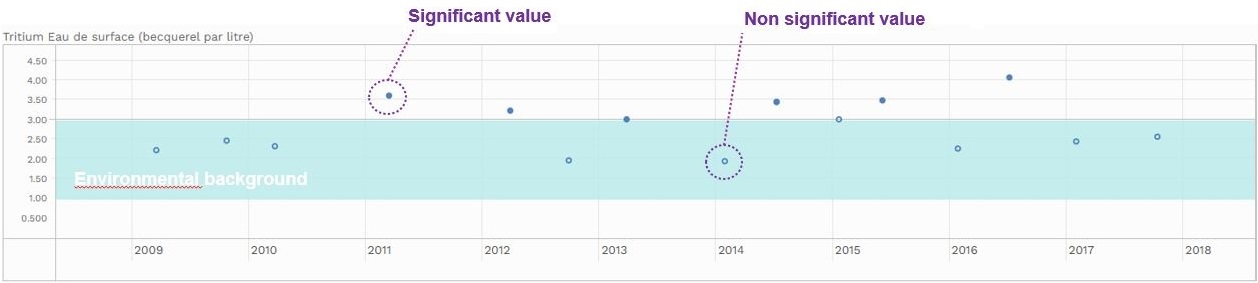
The distinction between ‘SIGNIFICANT’ and ‘NON-SIGNIFICANT’ measurments
When a measurement is represented in the graph by a full spot (significant value), it means that some artificial radioactivity has been detected.
A measurement represented by a solid circle is non-significant, i.e. the presence of radioactivity cannot be assessed with certainty, because of the measuring method used.
The units used
The Becquerel : legal and international unit of measurement used to quantify radioactivity. It is equal to one disintegration of a radioactive atom per second. To express specific or volumetric activities in environmental samples, Bq/kg (fresh or dry), Bq/L, or Bq/m³ are frequently used.
The Sievert : unit of measure corresponding to the impact of radioactivity on humans and living organisms, i.e. an estimation of exposure to radiation.
For more information, see the Metrology Concepts section.
 return to top
return to top




